Prepare your patients with the proper dose
VALTOCO is designed for prompt administration by anyone who needs a dose of diazepam to treat episodes of frequent seizure activity.1
VALTOCO is designed for prompt administration by anyone who needs a dose of diazepam to treat episodes of frequent seizure activity.1
The right solution starts with the right dose
If a dose is too low, suboptimal seizure control may occur; if a dose is too high, patients may have a greater risk of adverse events.2

VALTOCO has individualized dosing1
VALTOCO dosing by age and weight provides the right dose for pediatric patients
Dose based on weight for patients 2-5 years (0.5 mg/kg)
Dose based on weight for patients 6-11 years (0.3 mg/kg)
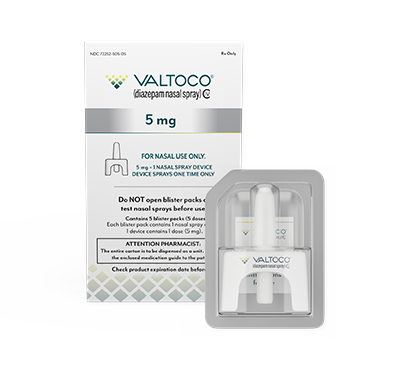
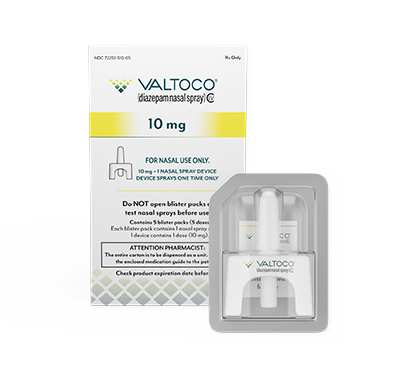
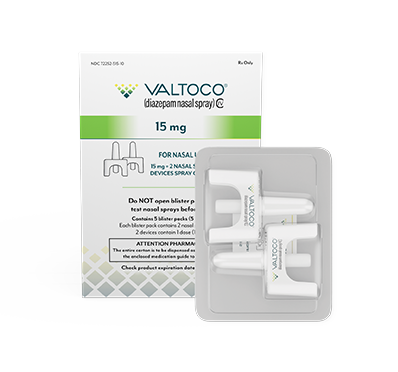
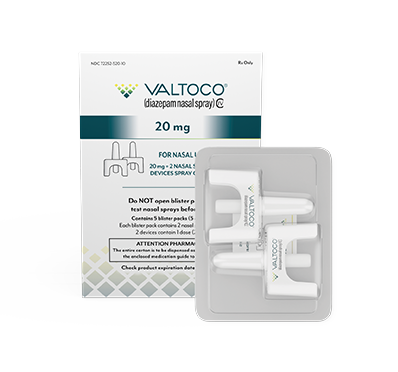
The 20 mg dose was not clinically evaluated in 2- to 5-year-old children.
VALTOCO dosing for older children and adult patients
Dose based on weight for patients 12+ years (0.2 mg/kg)
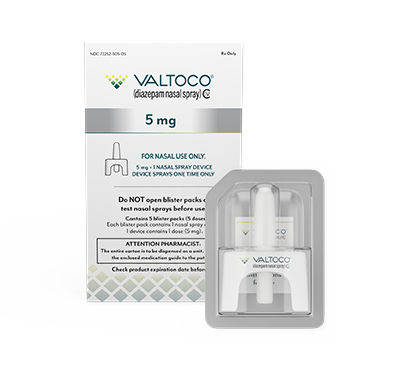
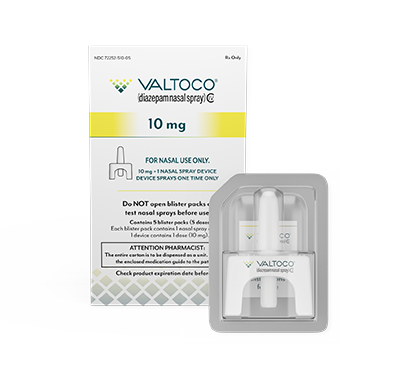
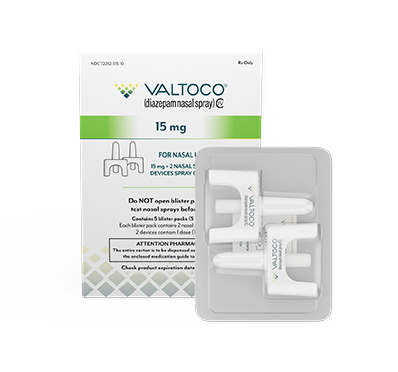
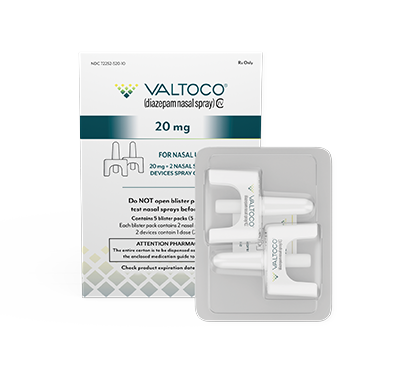
Majority of adult doses are 15 mg and 20 mg




The 20 mg dose was not clinically evaluated in 2- to 5-year-old children.




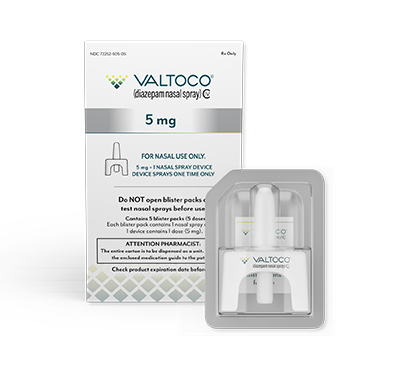
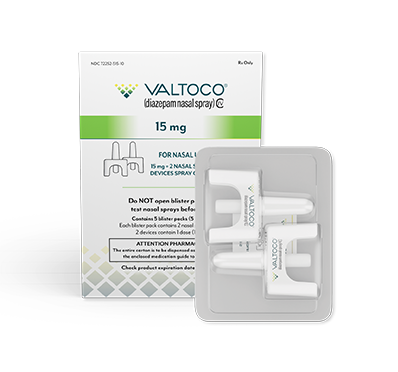
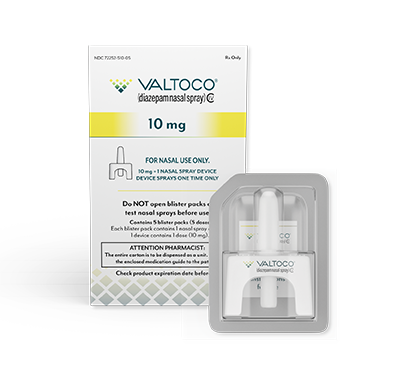
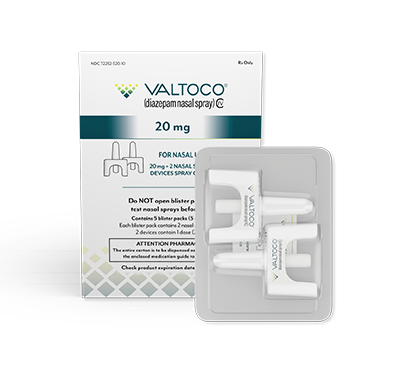
- Each box contains 5 doses
- 1 blister pack = 1 complete dose and includes Instructions for Use
- Do not use more than 2 doses of VALTOCO to treat a single episode. A second dose, when required, may be administered at least 4 hours after the initial dose. Do not use VALTOCO to treat more than 1 episode every 5 days or more than 5 episodes per month

VALTOCO is ready to use
Designed for prompt administration by anyone1
- Can be administered in an actively seizing patient, regardless of their position3
- Can be administered with the head in any position at any time during the seizure cluster cycle3
- Anyone who may need to give VALTOCO should review the full Instructions for Use before use
VALTOCO is easy to administer3
1. HOLD
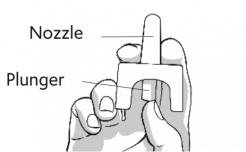
HOLD the nasal spray device with your thumb on the bottom of the plunger and your first and middle fingers on either side of the nozzle.
Do NOT press the plunger yet. If you press the plunger now, you will lose the medicine.
2. INSERT
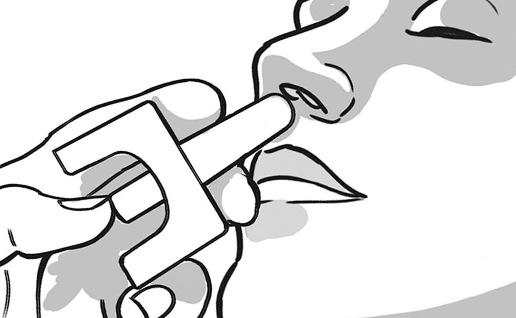
INSERT the tip of the nozzle into 1 nostril until your fingers, on either side of the nozzle, are against the bottom of the nose.
The nasal spray device can be used with the person’s head in any position.
3. PRESS

PRESS the bottom of the plunger firmly with your thumb to give VALTOCO.
The person does not need to breathe deeply when VALTOCO is given.
Throw away (discard) the nasal spray device and the blister pack after use.
1. HOLD

HOLD the nasal spray device with your thumb on the bottom of the plunger and your first and middle fingers on either side of the nozzle.
Do NOT press the plunger yet. If you press the plunger now, you will lose the medicine.
2. INSERT

INSERT the tip of the nozzle into 1 nostril until your fingers, on either side of the nozzle, are against the bottom of the nose.
The nasal spray device can be used with the person’s head in any position.
3. PRESS

PRESS the bottom of the plunger firmly with your thumb to give VALTOCO.
The person does not need to breathe deeply when VALTOCO is given.
Throw away (discard) the nasal spray device and the blister pack after use.
If giving the 15 mg or 20 mg dose, repeat the steps using the second device in the other nostril to give the full dose of VALTOCO.
Remember: If needed, a second dose may be given at least 4 hours after the initial dose.1
Patients should not use more than 2 doses of VALTOCO to treat a single episode.1
These are not the full Instructions for Use. Please see the complete Instructions for Use.
of care partners said it was “extremely easy” or “very easy” to be trained to administer VALTOCO4
Instructions for Use videos
See Instructions for Use videos for the specific steps on how to administer VALTOCO for 5 mg, 10 mg, 15 mg, or 20 mg doses.
There are also full Instructions for Use for the 5 mg and 10 mg dose or 15 mg and 20 mg dose.
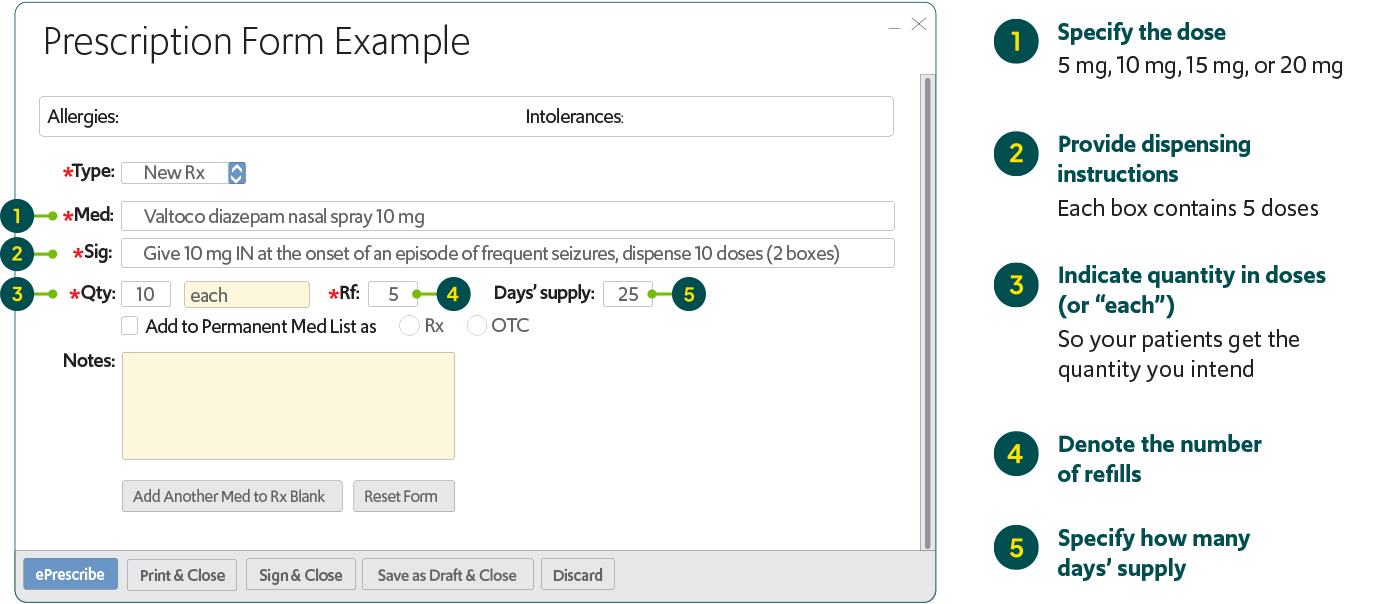
How to prescribe VALTOCO
When prescribing VALTOCO electronically, enter all the important information as shown below to save time for office staff, while ensuring the pharmacy provides exactly what you prescribed.

What patients can expect to receive in a box of VALTOCO
VALTOCO is available in 4 diazepam doses.
- 1 box of VALTOCO = 5 doses
- 1 blister pack = 1 complete dose and includes Instructions for Use
- Ready to use; no assembly required